Fecal Coliform and E coli
- are bacteria whose presence indicate that the water may be contaminated with human or animal wastes. Microbes in these wastes can cause short-term effects, such as diarrhea, cramps, nausea, headaches, or other symptoms.
Cryptosporidium - is a parasite that enters lakes and rivers through sewage and animal waste. This microbe has an outer shell that allows it to survive outside the body for long periods of time which makes it tolerant to many chlorine disinfectants. It causes cryptosporidiosis, a mild gastrointestinal disease. However, the disease can be severe or fatal for people with severely weakened immune systems. EPA and CDC have prepared advice for those with severely compromised immune systems who are concerned about Cryptosporidium.
Giardia Lamblia - is a parasite that enters lakes and rivers through sewage and animal waste. It causes gastrointestinal illness (e.g. diarrhea, vomiting, cramps). Giardia, like cryptosporidium, can survive long periods of time outside the body and is also difficult to treat with just basic chlorine disinfectants.
Coliform - bacteria are common in the environment and are generally not harmful. However, the presence of these bacteria in drinking water is usually a result of a problem with the treatment system or the pipes which distribute water. This indicates that the water may be contaminated with germs that can cause disease.
Turbidity - has no health effects. However, turbidity can interfere with disinfection because the particles can act as shields for viruses and bacteria and provide a medium for microbial growth. Turbidity may indicate the presence of disease causing organisms. These organisms include bacteria, viruses, and parasites that can cause symptoms such as nausea, cramps, diarrhea, and associated headaches.
Inorganic Contaminants
Arsenic - is a highly toxic heavy metal. Some people who drink water containing arsenic in excess of EPA's standard over many years could experience a wide range of serious problems. Health concerns include damage to the bladder, lungs, heart, kidney and liver. Arsenic can also harm the central & peripheral nervous system and circulatory system. Arsenic exposure has been linked to several types of cancers.
Fluoride - Many communities add fluoride to their drinking water to promote dental health. Each community makes its own decision about whether or not to add fluoride. EPA has set an enforceable drinking water standard for fluoride of 4 mg/L (some people who drink water containing fluoride in excess of this level over many years could get bone disease, including pain and tenderness of the bones). EPA has also set a secondary fluoride standard of 2 mg/L to protect against dental fluorosis.
Dental Fluorosis - in its moderate or severe forms, may result in a brown staining and/or pitting of the permanent teeth. This problem occurs only in developing teeth, before they erupt from the gums. Children under nine should not drink water that has more than 2 mg/L of fluoride.
Lead - typically leaches into water from plumbing in older buildings. Lead pipes and plumbing fittings have been banned since August 1998. Children and pregnant women are most susceptible to lead health risks. For advice on avoiding lead, see the how to remove lead in your drinking water fact sheet prepared by EPA.
Many water suppliers add a disinfectant to drinking water to kill germs such as giardia and e coli. Especially after heavy rainstorms, your water system may add more disinfectant to guarantee that these germs are killed.
Disinfectants
Chlorine - Some people who use drinking water containing chlorine in excess of EPA's standard could experience irritating effects to their eyes and nose as well as stomach discomfort.
Chloramines - are most commonly formed when chlorine and ammonia are added together to treat drinking water. Water that contains chloramines is usually safe as long as it meets EPA regulations. However, some people who are exposed to chloramines in excess of EPA's standard may experience irritating effects to their eyes, nose and stomach.
Chlorine Dioxide - is a water additive used to control taste and odor in water. Some infants and young children who drink water containing chlorine dioxide in excess of EPA's standard could experience nervous system effects as well as anemia. Similar effects may occur in fetuses of pregnant women who drink water containing chlorine dioxide in excess of EPA's standard.
Disinfection Byproducts - form when disinfectants added to drinking water to kill germs react with naturally-occuring organic matter in water.
Total Trihalomethanes - Some people who drink water containing trihalomethanes in excess of EPA's standard over many years may experience problems with their liver, kidneys, or central nervous systems, and may have an increased risk of getting cancer.
Haloacetic Acids - Some people who drink water containing haloacetic acids in excess of EPA's standard over many years may have an increased risk of getting cancer.
Bromate - Some people who drink water containing bromate in excess of EPA's standard over many years may have an increased risk of getting cancer.
Chlorite - Some infants and young children who drink water containing chlorite in excess of EPA's standard could experience nervous system effects as well as anemia. Similar effects may occur in fetuses of pregnant women who drink water containing chlorite in excess of EPA's standard.
Cryptosporidium - is a parasite that enters lakes and rivers through sewage and animal waste. This microbe has an outer shell that allows it to survive outside the body for long periods of time which makes it tolerant to many chlorine disinfectants. It causes cryptosporidiosis, a mild gastrointestinal disease. However, the disease can be severe or fatal for people with severely weakened immune systems. EPA and CDC have prepared advice for those with severely compromised immune systems who are concerned about Cryptosporidium.
Giardia Lamblia - is a parasite that enters lakes and rivers through sewage and animal waste. It causes gastrointestinal illness (e.g. diarrhea, vomiting, cramps). Giardia, like cryptosporidium, can survive long periods of time outside the body and is also difficult to treat with just basic chlorine disinfectants.
Coliform - bacteria are common in the environment and are generally not harmful. However, the presence of these bacteria in drinking water is usually a result of a problem with the treatment system or the pipes which distribute water. This indicates that the water may be contaminated with germs that can cause disease.
Turbidity - has no health effects. However, turbidity can interfere with disinfection because the particles can act as shields for viruses and bacteria and provide a medium for microbial growth. Turbidity may indicate the presence of disease causing organisms. These organisms include bacteria, viruses, and parasites that can cause symptoms such as nausea, cramps, diarrhea, and associated headaches.
Inorganic Contaminants
Arsenic - is a highly toxic heavy metal. Some people who drink water containing arsenic in excess of EPA's standard over many years could experience a wide range of serious problems. Health concerns include damage to the bladder, lungs, heart, kidney and liver. Arsenic can also harm the central & peripheral nervous system and circulatory system. Arsenic exposure has been linked to several types of cancers.
Fluoride - Many communities add fluoride to their drinking water to promote dental health. Each community makes its own decision about whether or not to add fluoride. EPA has set an enforceable drinking water standard for fluoride of 4 mg/L (some people who drink water containing fluoride in excess of this level over many years could get bone disease, including pain and tenderness of the bones). EPA has also set a secondary fluoride standard of 2 mg/L to protect against dental fluorosis.
Dental Fluorosis - in its moderate or severe forms, may result in a brown staining and/or pitting of the permanent teeth. This problem occurs only in developing teeth, before they erupt from the gums. Children under nine should not drink water that has more than 2 mg/L of fluoride.
Lead - typically leaches into water from plumbing in older buildings. Lead pipes and plumbing fittings have been banned since August 1998. Children and pregnant women are most susceptible to lead health risks. For advice on avoiding lead, see the how to remove lead in your drinking water fact sheet prepared by EPA.
Many water suppliers add a disinfectant to drinking water to kill germs such as giardia and e coli. Especially after heavy rainstorms, your water system may add more disinfectant to guarantee that these germs are killed.
Disinfectants
Chlorine - Some people who use drinking water containing chlorine in excess of EPA's standard could experience irritating effects to their eyes and nose as well as stomach discomfort.
Chloramines - are most commonly formed when chlorine and ammonia are added together to treat drinking water. Water that contains chloramines is usually safe as long as it meets EPA regulations. However, some people who are exposed to chloramines in excess of EPA's standard may experience irritating effects to their eyes, nose and stomach.
Chlorine Dioxide - is a water additive used to control taste and odor in water. Some infants and young children who drink water containing chlorine dioxide in excess of EPA's standard could experience nervous system effects as well as anemia. Similar effects may occur in fetuses of pregnant women who drink water containing chlorine dioxide in excess of EPA's standard.
Disinfection Byproducts - form when disinfectants added to drinking water to kill germs react with naturally-occuring organic matter in water.
Total Trihalomethanes - Some people who drink water containing trihalomethanes in excess of EPA's standard over many years may experience problems with their liver, kidneys, or central nervous systems, and may have an increased risk of getting cancer.
Haloacetic Acids - Some people who drink water containing haloacetic acids in excess of EPA's standard over many years may have an increased risk of getting cancer.
Bromate - Some people who drink water containing bromate in excess of EPA's standard over many years may have an increased risk of getting cancer.
Chlorite - Some infants and young children who drink water containing chlorite in excess of EPA's standard could experience nervous system effects as well as anemia. Similar effects may occur in fetuses of pregnant women who drink water containing chlorite in excess of EPA's standard.
Alkalinity Why Alkaline? Alkaline Q&A Acidity Self-Test
Proper Health starts with the correct acid-alkaline balance in your body. That’s why an Reverse Osmosis Alkaline Water filter system is so important. The pH level (acid - alkaline measurement) of our internal fluids affects every cell in our bodies. Extended acid imbalances of any kind can overwhelm your body, and lead to health complications.
Just as the body regulates its temperature in a rigid manner, so will it manage to preserve a very narrow pH range - especially in the blood. Alkaline water helps maintain a healthy pH. The body will go to such great lengths to maintain a blood pH of 7.365 that it will even create stress on other tissues, body systems, and organs to do so. Chronic acidity will interrupt all cellular activities and functions - it interferes with life itself.
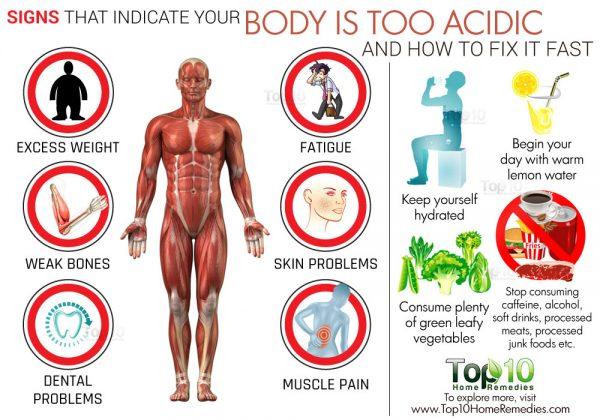
When the pH of the body gets out of balance (too acidic), we may experience low energy, fatigue, excess weight, poor digestion, aches and pains, and even more serious disorders. Imagine being able to avoid all those discomforts by simply drinking Alkaline Water and having your Alkaline Water System in the convenience of your home.
The cycle of acidity begins primarily as a result of three things:
Ingesting acids. Eating too many acidifying foods like processed sugar, meats, dairy, coffee, alcohol, etc. Create an acid ash in the body. These acids can overload the body’s ability to neutralize them
Creation of acids. Pathogens and microforms create acidifying toxins in the body. As the body becomes more and more acidic, bad bacteria, yeasts and other microforms proliferate in the body. Since these organisms are living, they eat as well as create resulting toxins. These toxins are often very acidifying.
Improper elimination of acids. Not all acids are the same; some are weak and some are strong. Weak acids like citric acid are much easier to neutralize than strong acids like uric acid. The body uses many systems in order to buffer acids including breath, mineral reserves, and fat. When the body’s buffering systems become compromised, excess acids build up.
The process of reestablishing acid-alkaline balance begins with proper diet and nutrition. This includes eating alkalizing foods (vegetables, low sugar fruits, etc.), super hydration (drinking plenty of alkaline water that is ionic and structured), and proper supplementation.

WHAT IS ORP?
Oxidation Reduction Potential or Redox is the activity or strength of oxidizers and reducers in relation to their concentration. Oxidizers accept electrons, reducers lose electrons. Examples of oxidizers are: chlorine, hydrogen peroxide, bromine, ozone, and chlorine dioxide. Examples of reducers are sodium sulfite, sodium bisulfate and hydrogen sulfide. Like acidity and alkalinity, the increase of one is at the expense of the other.
ORP stands for Oxidation-Reduction Potential. In practical terms, it is a measurement to oxidize contaminants. It's as simple as that. ORP is the only practical method we have to electronically monitor sanitizer effectiveness

There are many dangerous effects of oxidation- (the theft of an electron ) on the body's organs:
There are many dangerous effects of oxidation( the theft of an electron ) on the body's organs:
* Oxidation of the liver can lead to hepatitis, cirrhosis and cancer* Oxidation of the pancreas can lead to pancreatitis, diabetes and cancer* Oxidation of the kidney can lead to nephritis, nephrosis and cancer
Don't panic just yet! There is a way to protect your body's healthy tissue from oxidation caused by these free radicals, it’s called Alkaline Water. You must simply provide free electrons to the active oxygen radicals. This will neutralize their high oxidation potential and keep your healthy tissue safe from oxidation. All this will happen once you incorporate higher ph water like Alkaline Water into your diet.